News
How China’s CPEC debt trap has Ruined Pakistan’s Economy

The Pakistani economy is in shambles. Global creditors like the IMF, the World Bank, and bilateral partners are demanding long-overdue structural reforms, and the country is bracing for a massive financial default if they don’t get them.
These multilateral and bilateral creditors have made it clear that they will only provide financial assistance to Pakistan if the government enacts reforms; they cite the country’s low credit ratings, high debt sustainability risks, and weak macroeconomic situation as reasons for this stance.
Pakistan has massive debt—around US$125 billion outstanding to foreign creditors as of 2023, with about a third of that amount owed to China—which is the main cause of its economic problems.
Accusations that Beijing is pursuing “neo-colonial ambitions” through its alleged “Debt Trap Diplomacy” in Africa and Asia have once again come to the fore as a result of this.
According to experts, Beijing has been lending billions of dollars to economically fragile nations with big populations and a widening infrastructure funding gap. This is a sign of Beijing’s increasing financial influence.
As a result of this policy, many believed that China was actively encouraging the poorer nations to become more dependent on its loans, which were seen as predatory due to the ambiguous terms and circumstances that accompanied them.
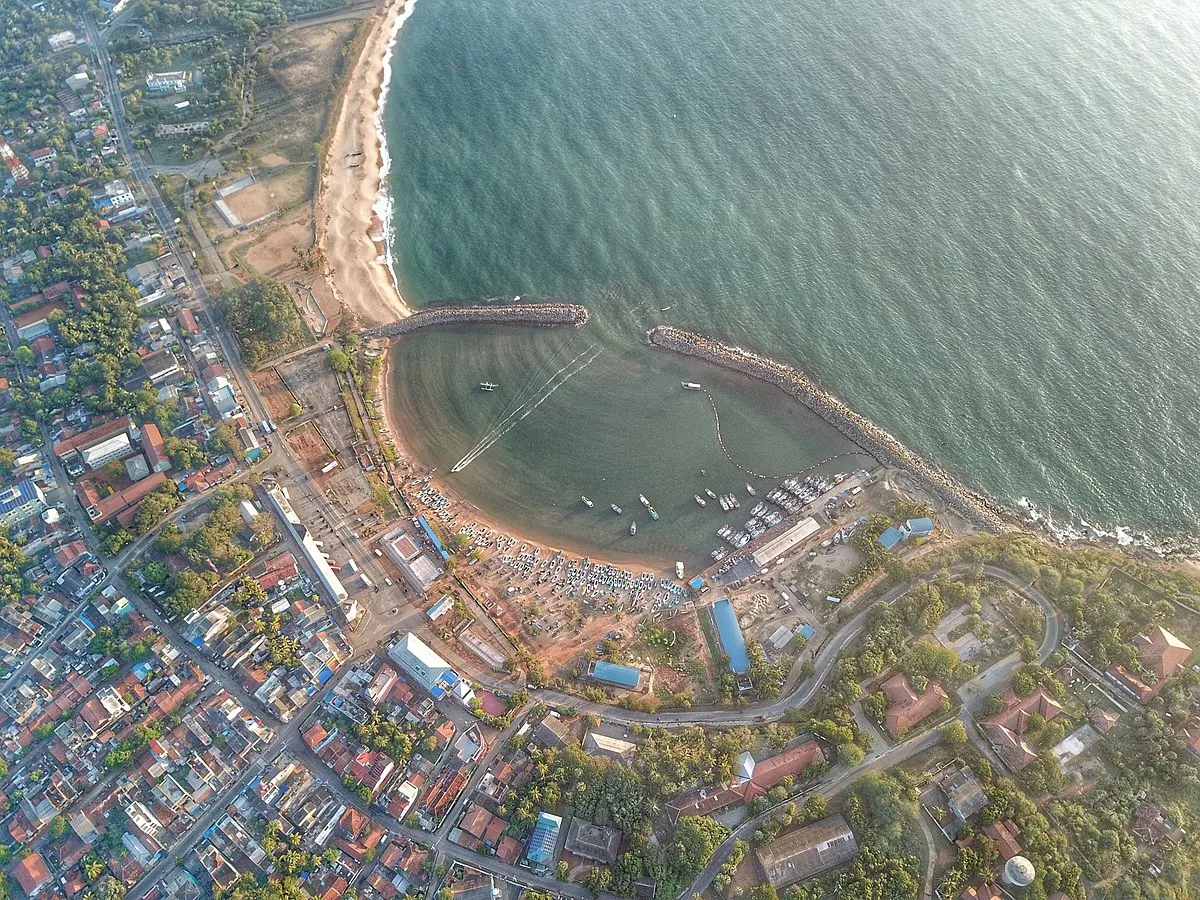
In his 2017 article “Debt Trap Diplomacy,” Indian strategist Brahma Chellaney argued that China’s military expanded its influence by coercing debtor nations into giving up important assets and resources through the strategic use of debt. As proof, consider Beijing’s 99-year lease of Sri Lanka’s Hambantota port and other infrastructure assets across Africa.

Chinese BRI Supports Nations Most in Need
It has come to light that China has enticed weak nations for its neocolonial ambitions through its much-touted transcontinental Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). The utilization of “Chinese companies…Chinese engineers, Chinese workers, and Chinese equipment” is typically an unspoken condition of Chinese loans to borrowing nations.
Several lower and middle-income states have accumulated nearly US$385 billion in ‘hidden debts,’ according to a US-based AidData Lab report reviewing 13,000 projects under the BRI.
These projects were mainly for infrastructure development, including constructing roads, highways, bridges, and hydropower dams. The report’s valuation was US$843 billion, covering 165 countries.
According to Keith Bradsher of the New York Times, “many nations are pushed to the brink” by a sluggish economy and increasing interest rates, causing many nations to struggle to service their debts.
For Pakistan, the picture is similar; after all, the nation owes more than a third of its total foreign debt to Beijing, making it the biggest debtor state to China.
Throughout its seven decades of existence, Pakistan has been governed by the military, which has led to misguided regional policy pursuits and a dismal socioeconomic infrastructure.
It served as an almost ideal model for Chinese enticement, which, under the BRI, pledged to improve and raise basic infrastructure.
With Pakistan’s 2013 accession to the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China’s predatory lending reached exponential heights; the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), the project’s most vital component, began with an initial budget of $45 billion but has now ballooned to more than $62 billion.
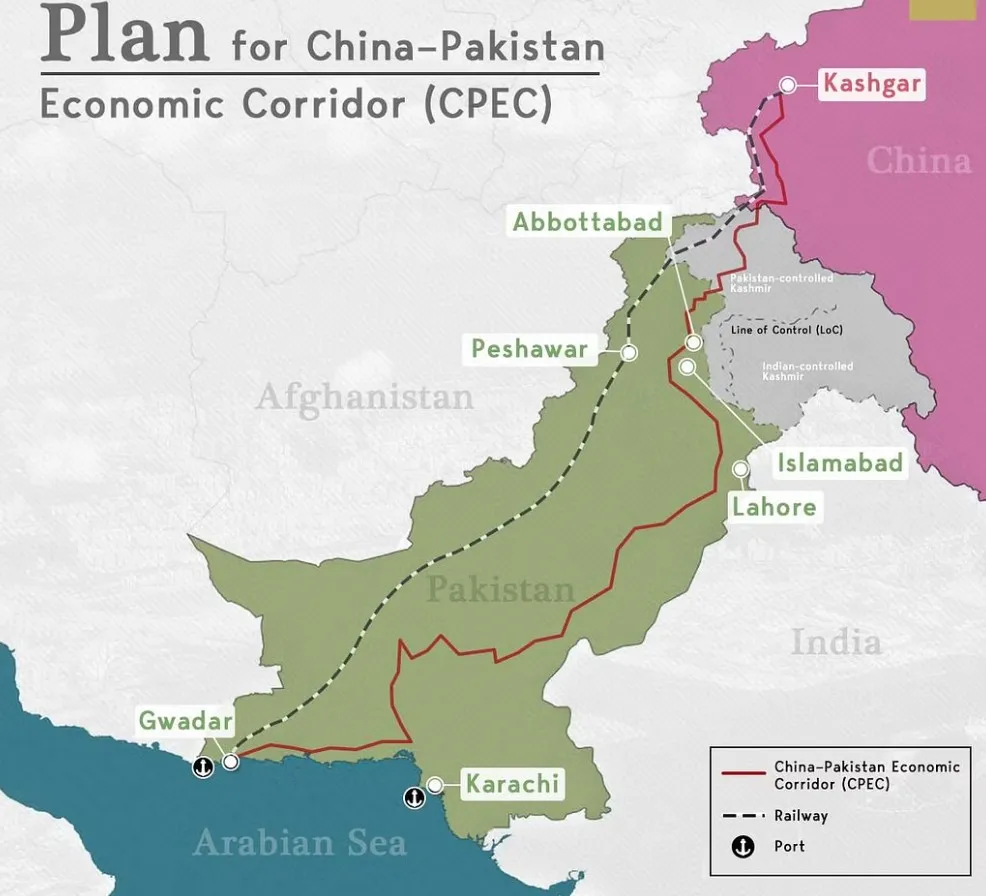
The Almost Perfect Debt Trap in Pakistan
With an estimated project cost of over US$25 billion, the Pakistani portion of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is the largest contributor to Pakistan’s mounting foreign debt. This means that Islamabad owed Chinese creditors this amount of money upfront.
Most of China’s aid to Pakistan has gone toward “infrastructure and energy investments,” but the character of this aid has been particularly noteworthy.
Despite what successive Pakistani governments supported by the military establishment would have you believe, Beijing’s investments in Pakistan were loans and not handouts, contrary to widely held beliefs and skillfully crafted public views.
Much more worrisome is that Pakistan obtained these loans at flat commercial rates above 5% and, in many instances, over 7%—much more than other international financial lenders like the IMF, which lends at 2%.
Islamabad is having trouble keeping up with its debt service because of the debt spiral that Pakistan has fallen into due to these much higher interest rates. Debt servicing in Pakistan has not been able to repay the same interest rates as original borrowings, a sign of how viciously the country’s debt has accumulated.
Pakistan owes China $40 billion; even using a modest 5% interest rate, the interest component of this debt would still leave the country with $2 billion.
As an example, according to the State Bank of Pakistan, Pakistan will have to pay back $20.81 billion (PKR 792 lakh crore) in foreign debt in Fiscal Year 2023. This figure includes a massive interest payment of $4.42 billion (PKR12.46 lakh crore).
Because of its low credit score and its inability to meet the demands of foreign lenders—including micro-cum-macro economic reforms and an improvement in its tax collection regime—the country is dependent on China for financial support and must keep vital sovereign wealth reserves on hand to guarantee its short-term viability.
Repaying the previous loans at the interest rates set by Beijing—mainly commercial lending rates—will require Pakistan to take out new loans from China. An example is the US$600 million loan that Pakistan reportedly discussed with the Bank of China and the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) on November 8.
This pattern persists from 2017, when Pakistan began to borrow money from Beijing to repay the debts it had received as “grants” under the CPEC for development.
Pakistan’s dire economic predicament, which could lead to a financial default, is a result of its massive debt, most of which is owed to Chinese lenders.
China appears pleased to keep Islamabad afloat like a sick patient on essential ventilator support, effectively encircling Pakistan in a vicious debt trap loop.
Despite appearances, thanks to this generous support, China is strategically positioned to dictate terms and acquire key strategic assets. This suggests a dismal future for the nation, which can affect both the country and the surrounding area.

News
Google’s Search Dominance Is Unwinding, But Still Accounting 48% Search Revenue

Google is so closely associated with its key product that its name is a verb that signifies “search.” However, Google’s dominance in that sector is dwindling.
According to eMarketer, Google will lose control of the US search industry for the first time in decades next year.
Google will remain the dominant search player, accounting for 48% of American search advertising revenue. And, remarkably, Google is still increasing its sales in the field, despite being the dominating player in search since the early days of the George W. Bush administration. However, Amazon is growing at a quicker rate.
Google’s Search Dominance Is Unwinding
Amazon will hold over a quarter of US search ad dollars next year, rising to 27% by 2026, while Google will fall even more, according to eMarketer.
The Wall Street Journal was first to report on the forecast.
Lest you think you’ll have to switch to Bing or Yahoo, this isn’t the end of Google or anything really near.
Google is the fourth-most valued public firm in the world. Its market worth is $2.1 trillion, trailing just Apple, Microsoft, and the AI chip darling Nvidia. It also maintains its dominance in other industries, such as display advertisements, where it dominates alongside Facebook’s parent firm Meta, and video ads on YouTube.
To put those “other” firms in context, each is worth more than Delta Air Lines’ total market value. So, yeah, Google is not going anywhere.
Nonetheless, Google faces numerous dangers to its operations, particularly from antitrust regulators.
On Monday, a federal judge in San Francisco ruled that Google must open up its Google Play Store to competitors, dealing a significant blow to the firm in its long-running battle with Fortnite creator Epic Games. Google announced that it would appeal the verdict.
In August, a federal judge ruled that Google has an illegal monopoly on search. That verdict could lead to the dissolution of the company’s search operation. Another antitrust lawsuit filed last month accuses Google of abusing its dominance in the online advertising business.
Meanwhile, European regulators have compelled Google to follow tough new standards, which have resulted in multiple $1 billion-plus fines.

Pixa Bay
Google’s Search Dominance Is Unwinding
On top of that, the marketplace is becoming more difficult on its own.
TikTok, the fastest-growing social network, is expanding into the search market. And Amazon has accomplished something few other digital titans have done to date: it has established a habit.
When you want to buy anything, you usually go to Amazon, not Google. Amazon then buys adverts to push companies’ products to the top of your search results, increasing sales and earning Amazon a greater portion of the revenue. According to eMarketer, it is expected to generate $27.8 billion in search revenue in the United States next year, trailing only Google’s $62.9 billion total.
And then there’s AI, the technology that (supposedly) will change everything.
Why search in stilted language for “kendall jenner why bad bunny breakup” or “police moving violation driver rights no stop sign” when you can just ask OpenAI’s ChatGPT, “What’s going on with Kendall Jenner and Bad Bunny?” in “I need help fighting a moving violation involving a stop sign that wasn’t visible.” Google is working on exactly this technology with its Gemini product, but its success is far from guaranteed, especially with Apple collaborating with OpenAI and other businesses rapidly joining the market.
A Google spokeswoman referred to a blog post from last week in which the company unveiled ads in its AI overviews (the AI-generated text that appears at the top of search results). It’s Google’s way of expressing its ability to profit on a changing marketplace while retaining its business, even as its consumers steadily transition to ask-and-answer AI and away from search.

Google has long used a single catchphrase to defend itself against opponents who claim it is a monopoly abusing its power: competition is only a click away. Until recently, that seemed comically obtuse. Really? We are going to switch to Bing? Or Duck Duck Go? Give me a break.
But today, it feels more like reality.
Google is in no danger of disappearing. However, every highly dominating company faces some type of reckoning over time. GE, a Dow mainstay for more than a century, was broken up last year and is now a shell of its previous dominance. Sears declared bankruptcy in 2022 and is virtually out of business. US Steel, long the foundation of American manufacturing, is attempting to sell itself to a Japanese corporation.
SOURCE | CNN
News
2024 | Supreme Court Won’t Hear Appeal From Elon Musk’s X Platform Over Warrant In Trump Case

Washington — Trump Media, The Supreme Court announced Monday that it will not hear an appeal from social media platform X about a search warrant acquired by prosecutors in the election meddling case against former President Donald Trump.
The justices did not explain their rationale, and there were no recorded dissents.
The firm, which was known as Twitter before being purchased by billionaire Elon Musk, claims a nondisclosure order that prevented it from informing Trump about the warrant obtained by special counsel Jack Smith’s team violated its First Amendment rights.
The business also claims Trump should have had an opportunity to exercise executive privilege. If not reined in, the government may employ similar tactics to intercept additional privileged communications, their lawyers contended.
Supreme Court Won’t Hear Appeal From Elon Musk’s X Platform Over Warrant In Trump Case
Two neutral electronic privacy groups also joined in, urging the high court to hear the case on First Amendment grounds.
Prosecutors, however, claim that the corporation never shown that Trump utilized the account for official purposes, therefore executive privilege is not a problem. A lower court also determined that informing Trump could have compromised the current probe.

Trump utilized his Twitter account in the weeks preceding up to his supporters’ attack on the Capitol on January 6, 2021, to spread false assertions about the election, which prosecutors claim were intended to create doubt in the democratic process.
The indictment describes how Trump used his Twitter account to encourage his followers to travel to Washington on Jan. 6, pressuring Vice President Mike Pence to reject the certification, and falsely claiming that the Capitol crowd, which battered police officers and destroyed glass, was peaceful.
Supreme Court Won’t Hear Appeal From Elon Musk’s X Platform Over Warrant In Trump Case
That case is now moving forward following the Supreme Court’s verdict in July, which granted Trump full immunity from criminal prosecution as a former president.
The warrant arrived at Twitter amid quick changes implemented by Musk, who bought the company in 2022 and has since cut off most of its workforce, including those dedicated to combating disinformation and hate speech.
SOURCE | AP
News
The Supreme Court Turns Down Biden’s Government Appeal in a Texas Emergency Abortion Matter.

(VOR News) – A ruling that prohibits emergency abortions that contravene the Supreme Court law in the state of Texas, which has one of the most stringent abortion restrictions in the country, has been upheld by the Supreme Court of the United States. The United States Supreme Court upheld this decision.
The justices did not provide any specifics regarding the underlying reasons for their decision to uphold an order from a lower court that declared hospitals cannot be legally obligated to administer abortions if doing so would violate the law in the state of Texas.
Institutions are not required to perform abortions, as stipulated in the decree. The common populace did not investigate any opposing viewpoints. The decision was made just weeks before a presidential election that brought abortion to the forefront of the political agenda.
This decision follows the 2022 Supreme Court ruling that ended abortion nationwide.
In response to a request from the administration of Vice President Joe Biden to overturn the lower court’s decision, the justices expressed their disapproval.
The government contends that hospitals are obligated to perform abortions in compliance with federal legislation when the health or life of an expectant patient is in an exceedingly precarious condition.
This is the case in regions where the procedure is prohibited. The difficulty hospitals in Texas and other states are experiencing in determining whether or not routine care could be in violation of stringent state laws that prohibit abortion has resulted in an increase in the number of complaints concerning pregnant women who are experiencing medical distress being turned away from emergency rooms.
The administration cited the Supreme Court’s ruling in a case that bore a striking resemblance to the one that was presented to it in Idaho at the beginning of the year. The justices took a limited decision in that case to allow the continuation of emergency abortions without interruption while a lawsuit was still being heard.
In contrast, Texas has been a vocal proponent of the injunction’s continued enforcement. Texas has argued that its circumstances are distinct from those of Idaho, as the state does have an exemption for situations that pose a significant hazard to the health of an expectant patient.
According to the state, the discrepancy is the result of this exemption. The state of Idaho had a provision that safeguarded a woman’s life when the issue was first broached; however, it did not include protection for her health.
Certified medical practitioners are not obligated to wait until a woman’s life is in imminent peril before they are legally permitted to perform an abortion, as determined by the state supreme court.
The state of Texas highlighted this to the Supreme Court.
Nevertheless, medical professionals have criticized the Texas statute as being perilously ambiguous, and a medical board has declined to provide a list of all the disorders that are eligible for an exception. Furthermore, the statute has been criticized for its hazardous ambiguity.
For an extended period, termination of pregnancies has been a standard procedure in medical treatment for individuals who have been experiencing significant issues. It is implemented in this manner to prevent catastrophic outcomes, such as sepsis, organ failure, and other severe scenarios.
Nevertheless, medical professionals and hospitals in Texas and other states with strict abortion laws have noted that it is uncertain whether or not these terminations could be in violation of abortion prohibitions that include the possibility of a prison sentence. This is the case in regions where abortion prohibitions are exceedingly restrictive.
Following the Supreme Court’s decision to overturn Roe v. Wade, which resulted in restrictions on the rights of women to have abortions in several Republican-ruled states, the Texas case was revisited in 2022.
As per the orders that were disclosed by the administration of Vice President Joe Biden, hospitals are still required to provide abortions in cases that are classified as dire emergency.
As stipulated in a piece of health care legislation, the majority of hospitals are obligated to provide medical assistance to patients who are experiencing medical distress. This is in accordance with the law.
The state of Texas maintained that hospitals should not be obligated to provide abortions throughout the litigation, as doing so would violate the state’s constitutional prohibition on abortions. In its January judgment, the 5th United States Circuit Court of Appeals concurred with the state and acknowledged that the administration had exceeded its authority.
SOURCE: AP
SEE ALSO:
Could Last-Minute Surprises Derail Kamala Harris’ Campaign? “Nostradamus” Explains the US Poll.
-

 News4 years ago
News4 years agoLet’s Know About Ultra High Net Worth Individual
-
Entertainment2 years ago
Mabelle Prior: The Voice of Hope, Resilience, and Diversity Inspiring Generations
-
News11 years ago
Enviromental Groups Tell Mekong Leaders Lao Dam Evaluation Process Flawed
-

 Health4 years ago
Health4 years agoHow Much Ivermectin Should You Take?
-

 Tech3 years ago
Tech3 years agoTop Forex Brokers of 2023: Reviews and Analysis for Successful Trading
-

 Lifestyles3 years ago
Lifestyles3 years agoAries Soulmate Signs
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoWhat Should I Do If Disney Plus Keeps Logging Me Out of TV?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoCan I Buy Ivermectin Without A Prescription in the USA?


